Table of Contents
Netzer Playground - Simply develop Ethernet devices
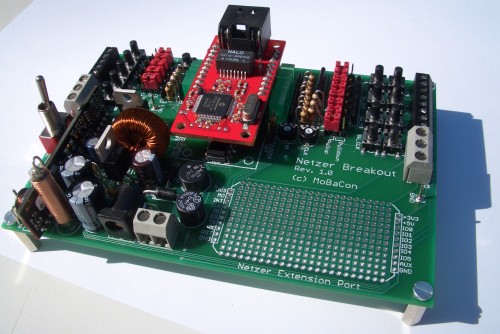 The Netzer Playground enables quick development of circuits around the ethernet gateway Netzer from MoBaCon. Netzer is simply put into the prepared socket.
The Netzer Playground enables quick development of circuits around the ethernet gateway Netzer from MoBaCon. Netzer is simply put into the prepared socket.
The image shows a functional block diagram of the board.
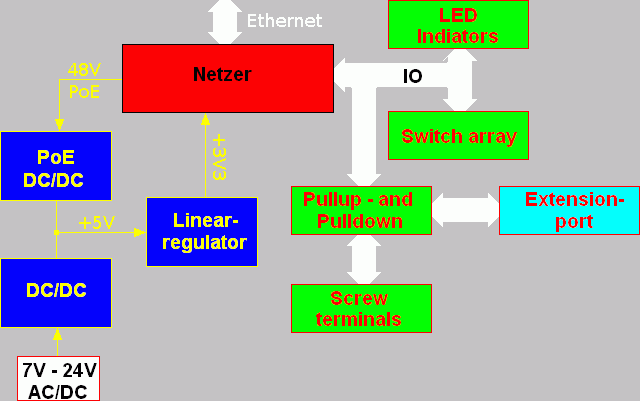
The extension port has an important role. Depending on the application several extension boards can be put in the socket. Extension boards for LCD and domestic (relays, temperatur and light sensors, opto decoupled inputs) are under development.
Circuit Description
Netzer socket and extension port
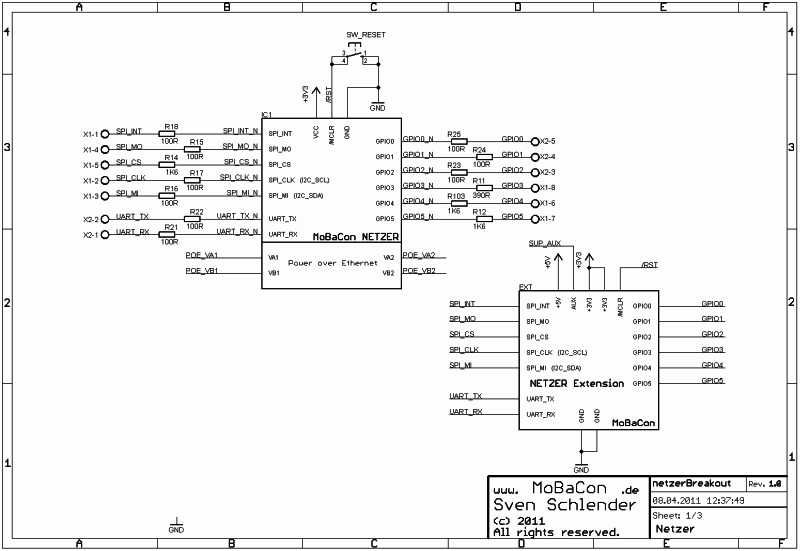
Sheet 1 shows the slot for Netzer and extension port. The Netzer can be directly soldered or plugged in via sockets. All IO pins of Netzer are protected against high input currents with serial 100 Ω resistors. SW_Reset pulls the Netzer reset pin to ground and generates a system reset at the Netzer and at a potentially connected board at the extension port which can be plugged in via two 10-pin headers with 2 mm grid. Netzer is supplied with the 3.3V generated before. For a flexible Extension Port all Netzer pins and all available voltages (also SUP_AUX, see below) are connected.
Power supply
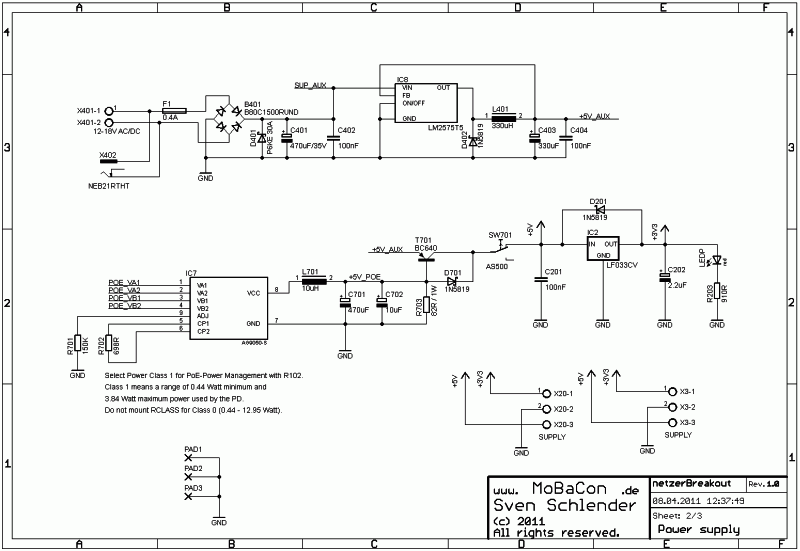
Sheet 2 shows the power supply. The input voltage (6 V – 24 V, AC or DC) from X401 is protected against reverse polarity (B401), ESD (D401) and short circuits (F401). The voltage (SUP_AUX) is connected to the extension port. The upper part generates from DC or AC with the switching regulator IC4 (in combination with D401, L401 and electrolytes C402 and C403) a stable 5V (+5V_AUX). A switching regulator was chosen for a wide voltage input range. An extra heat sink is not required.
Alternatively, a Power-over-Ethernet supply device (Silver Telecom ones are used here) can be mounted. The 48V source voltage (POE_VA1, _VA2, _VB1 and _VB2) is picked directly from Netzer. The power supply generates +5V (optional galvanically isolated –Ag9050-S or galvanically connected Ag8005-S). L701, C701 and C702 are used for low ripple. R702 is a resistance indicating the PoE-device the power class required for the power sourcing equipment (Class 0, see Table 1).
| Power CLASS | Programming Resistance (Ohms) | Min Power (W) | Max Power (W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Do not assemble | 0.44 | 12.95 |
| 1 | 698 ±1% | 0.44 | 3.84 |
| 2 | 383 ±1% | 3.84 | 6.49 |
| 3 | 249 ±1% | 6.49 | 12.95 |
Table 1: Power classes for Ag9050 or Ag8005 (Source: from data sheet)
D701, D702, T401 and R401 are used for prioritized O-ring of the PoE voltage for +5V_AUX. Transistor T401 is open for +5V_AUX only if there is no PoE voltage via R401. PoE has the highest priority. R701 (A for Ag9050, B for Ag8005) compensates the voltage drop of D702 - the PoE voltage is adjusted to 5.2V.
The voltage behind T401 is the first power supply of +5V switchable through SW_P. The linear voltage regulator IC2 converts the +5V to 3.3V. LED_P indicates this voltage.
Ground and power supplies are quickly accessible via wire pads and screw terminals (X10 and X20).
IO
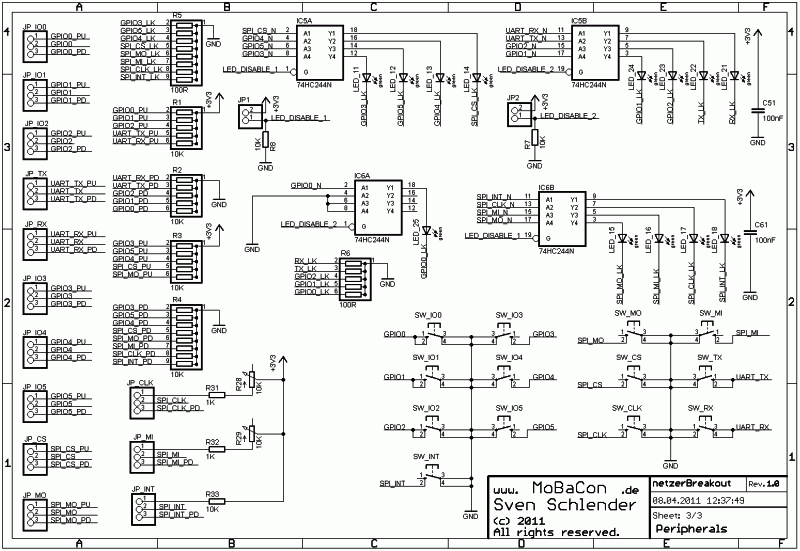
Sheet 3 shows the Breakout parts for testing Netzer IOs. All IOs are connected to LEDs via driver (IC5 and IC6). The LEDs are used as port state indicators. R5 and R6 adjust the LED current. With jumpers JP1 and JP2 the LED drivers can be deactivated as well.
Each IO pin is connected to the middle pin of a three-pole jumper. A jumper bridge chooses between a 10 kΩ pull-up (R1 and R3) or pull-down resistor (R2 and R4). The IOs SPI_CLK and SPI_MI are an exception because their pull-ups can be adjusted by a potentiometer (R28 and R29) in a range between 1 kΩ – 11 kΩ. That can be useful if the Netzer I2C mode is used. In that mode the resistors have to be adjusted for an intended bus frequency.
Last but not least the switches named SW_XX can pull any IO to ground. A configured Netzer input and an activated pull-up are necessary for using these switches.
Module
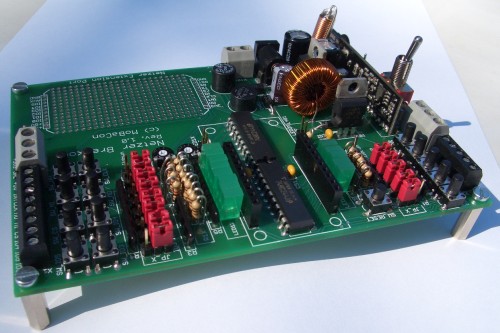
The module has the dimensions 134 mm x 90 mm. All delivered parts are THT parts. The level for assembly is estimated as medium difficult, because of the amount of parts to assemble.
The board has four mounting holes for distance bolts or enclosure.
Shopping
Currently not available.